Block Coding | Everything You Need to Know
Introduction (History Of Block-based Coding)
Computer programming is a method for these instructions, and computer programmers develop code to solve issues or complete tasks. Block coding is a programming element that converts text-based software code into a visual block format to reduce potential errors. Users can construct games, apps, and other programs by dragging and dropping visual block programming representations of text-based code (event listeners, functions, variables, audio, and more) into the code editor.
The first block coding language, Scratch, was developed at MIT in 2003 to teach schoolchildren how to code. Since then, dozens, if not hundreds, of schools and children's learning programs have adopted block coding as the most successful method of teaching coding for kids. Rather than memorising, it leaned heavily on visual aids and practical sequential reasoning.

What do you mean by “blocks?”
The "chunks" or "pieces" of instructions that a user assembles to educate their invention on what to do are referred to as blocks. Sprites move and turn for the sprite itself, other sprites, or a specific position using Motion Blocks.
For example, developers can order a sprite to take 10 steps forward or turn 15 degrees to the right with just one block. Blocks are used to alter a sprite's appearance. They can make a sprite say or think anything, change costumes or backdrops, or even change the scale or graphic effects of a sprite.
Sound blocks are used to add sounds to a tale or game, as well as adjust sound effects such as pitch and change the level of different sounds.
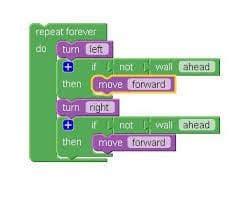
What is Block Coding?
The puzzle-piece metaphor is used in block coding to provide visual indications to the user about how and where commands can be combined and used. Youngsters as young as five can use block coding environments, but most target children ages eight to sixteen. The environment stops two instructions from snapping together to generate a valid assertion if they cannot be linked.
What can we create with drag-and-drop block coding?
Kids may let their imaginations run wild with block-based coding in a tool like Scratch, creating an unlimited number of sprites and bringing their creations to life with animation and storytelling.
Scratch, for example, allows children to create:
Clicker games involve clicking to win points, such as popping balloons. As you click on each balloon, a new one of a different hue appears at a different location on the screen.
Example of a scratch clicker game:
Players control a character who is "chasing" another character or object in chase games. It could, for example, be an octopus attempting to catch a fish swimming around aimlessly on the screen.
Pong games are exactly what they sound like: the classic configuration with a paddle and a ball.
Learn more about Game on Scratch!
Benefits Of Block-based Coding
1.Syntax Free Programming
Block-based coding relieves the burden of complex syntax and allows the programmer to concentrate on difficult areas that logically require more attention. Unlike text-based programming, the most excellent thing about syntax-free programming is that it avoids simple and minor syntax errors, which unnecessarily increase development time rather than decrease. Block coding websites provide an excellent platform for beginners, especially coding for kids, to explore this method and enhance their programming skills without the hassle of syntax issues.
2. Easy to use
Block-based coding allows users to focus on the logic of their code by removing the possibility of syntax errors because nearly no typing is necessary; snapping blocks together helps to prevent spelling and typo problems, as well as numerous syntax errors, by preventing blocks from being constructed in ineffective ways.
3. Graphical Programming
Visual programming was intended to assist humans with images, making learning much simpler and plainer. Its purpose is to make programming approachable at three different levels. Syntax eliminates syntactic errors by using icons/blocks, forms, and diagrams. Semantics uses metadata to explain the program used in the code. Stimulation uses visual mechanisms to test a program's behaviour or state.
4. Quick Results
Block-based coding gets the job done faster! Instead of learning how to enter lines of code in highly specific formats, pupils should focus on understanding the core functions of the various blocks. You can make a fun game or animation even if you only know how to utilize a few blocks. Making text appear on a screen is a common first step in text-based coding lessons.
5. No need to Memorize huge codes
In a block code environment, each of the puzzle parts can be chosen from a list. The list is usually divided into categories based on the types of activities that blocks perform—math, time, logic, and so on. Unlike most traditional text-based coding languages, where users must memorize all of the rules and code snippets, block programming provides an orderly list of components, allowing users to utilize the language without having to memorize every part.
6. Learning is reinforced through co-creating knowledge.
When students are allowed to share and discuss their work, the feedback they get from their peers reinforces their learning. Know more about the benefits of learning to code!
7.Simple to operate
Block-based programming languages are easy to use. Block-based coding allows children to quickly design a tangible object with which they can interact. This motivates them to continue learning.
Block-based coding is popular among educators for a variety of reasons-
The entry hurdle is low. Drag and drop blocks to run the program. Both teachers and students will find it simple to comprehend.
Low student frustration: there are no syntax errors, which is a drawback of text-based programming.
Easy for New Teachers: There is a well-known scarcity of computer science teachers ( in the US). Teachers who did not major in computer science in college can rapidly take up and understand block coding games for kids.
The book details all the programming concepts, including operators, events, control structures, and more.
It encourages experimentation. Good programmers aren't afraid to mess about with the code. Block coding for kids is so simple that it urges users to try out a few blocks and see what occurs!
Block-based programming has simplified the programming process, especially for youngsters and novice coders.
Few of the cons of block coding are:
Text-based coding makes detecting and fixing problems easier because code elements are grouped. For young learners, block-based coding offers a more concrete coding experience. Not only on-screen but also in children's hands with Scratch Cards, a set of cards that provides a tactile, visual depiction of many coding ideas and teachings.
There are only a few options for debugging. While Scratch allows for some debugging, debugging in a text-based environment is fundamentally different. A "step by step" debug with breakpoints, for example, does not exist in any block-based program that we are aware of.
A far broader range of data structures is supported. Block coding vs. text coding. What works in block-based coding might pose problems for first-time coders who have never had to worry about syntax errors.
Students in a block environment are less likely to test new instructions sequentially. Instead, it's usual for children to assemble many blocks before determining whether or not their instructions are correct. This is only natural, given the creative and enjoyable nature of using blocks.
Read more: Coding Games for Kids
Examples of Block Code
The fundamental purpose behind block codes is to give the user or recipient of such codes inputs with which they can fix any potential code issues without having to contact the code's source. In telecommunications, the principle is to encode a message in such a way that the recipient may only rectify a small number of errors before the message is considered unacceptable. This operation eliminates the risk of the message being retransmitted, which wastes time and resources.
A variety of block programming types are utilized, including:

- Reed-Solomon codes
- Hamming codes
- Sound blocks
- Motion blocks
- Loop blocks
- Hadamard codes
- Reed-Muller codes
Block Coding Websites for Kids
Blockly
Cost: Free
Blockly teaches kids block coding through increasingly difficult puzzles that they can solve with intuitive tools. To solve each task, children must drag and drop the code pieces.
Tynker
Cost: Free & paid
After completing the lessons, students can construct their puzzles, games, websites, and apps. The Tynker website's block-based programming section is completely free to use.
Code. org
Cost: Free
Code. org-For student coders all across the world, Code.org is the original home of the popular Hour of Code. It's divided into sections for grades K-5 and 6-12, with interactive instructions and entertaining projects. Students begin by learning block programming before moving on to Javascript, HTML, and CSS.
Stencyl
Cost: Free & paid
Stencyl is a block programming language for kids' websites with supercharged functionality! Its basic block programming language allows users to create games that can be released on various platforms.
Bitsbox
Cost: Free & paid
Bitsbox is one of the best solutions for providing hands-on experience to children. Their business strategy is subscription-based, and each month, they deliver a coding-themed project so that students can practice their skills on real-world projects and learn the basics.
Game Salad
Cost: Free & paid
It is a more advanced platform than Scratch or Hopscotch, and it's a fun way to get older students interested in coding for kids. The block-based programming framework is especially helpful for those who aren't comfortable with it. Children may make their games by dragging and dropping game items into their workspace and then adding rules to control how the game runs. This stage is ideal for bolstering game design strategies, as well as perseverance and critical thinking.
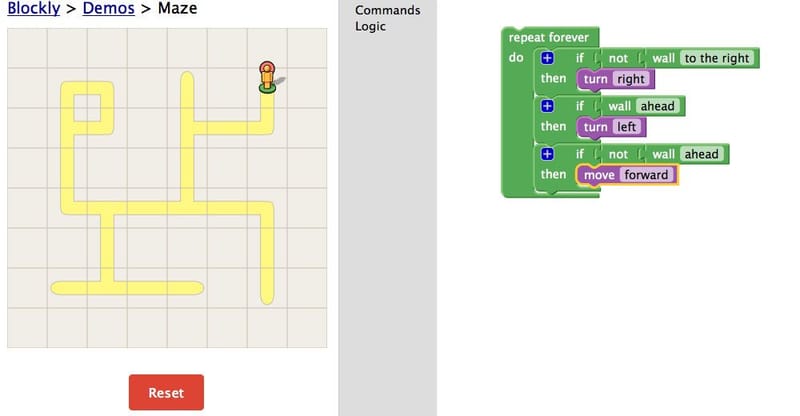
VEXcodeVR
Cost: Free
Students use VEXcode VR to program a virtual robot to navigate various 3D virtual playgrounds, such as a walled maze, an art canvas, and a grid universe. Educators create a series of tasks that provide outstanding challenges.
Block-Based Coding Builds Games, Software, & More!
Games
The most popular use of block coding languages is to create games. Depending on the coder, block programming can range from simple to complex. Mazes, clicking games, chasing games, pong games, and even full-fledged adventure games are all possibilities for kids, often found on popular block coding websites.
Programs
For coding for kids, several robotics kits for children employ block coding languages. That means your youngster can program their robot to move, perform tasks, make sounds, and do other things. Several kits also allow you to program in either a block coding-based or text-based language.
Animations
Most of the new block coding for kids begins by making an animation. Simple animations include a single screen with animated characters (sprites) with motion and sound. More complicated animations can span numerous screens and tell a complete tale. Multiple characters, clothes, dialogue bubbles, music, and many types of motion can all be included.
Learn Block-Based Programming- Conclusion
Codeyoung is an interactive and educational platform for kids to learn block-based programming. One of the most significant obstacles when it comes to block coding for kids is that many people feel it is only for individuals in technical fields. Codeyoung provides an interface through which block coding is accessible and easy to learn for everyone, and anyone who wants to learn it can. You can also explore a range of block coding websites to support your learning journey.
We have mentors that are familiar with the foundations of coding and have begun teaching children to block coding. The concept of the drag and drop option is so straightforward that no prior knowledge of coding is required. You can book a FREE DEMO CLASS for your kids on this platform! The block coding language learning aspect is so engaging and enjoyable that students are constantly eager to learn more. Explore our recommended block coding website for additional resources and fun challenges!
Frequently Asked Questions
1) What is block coding?
Block coding is a visual approach to teaching coding. All the students have to do is click and drag the various code pieces together. This graphic representation of block-based programming is a useful teaching tool for demonstrating how different coding pieces interact.
2) Is Block Coding real coding?
Block coding is a good place to start because it will help you understand the fundamentals. Block coding helps you better understand programming logic and design. It is the first step to start text coding later. For novices, a block-coding environment increases learnability. Embedding algorithmic patterns into blocks favours recognition over recollection and decreases cognitive burden. The blocks also help to prevent errors and improve understanding of the program's structure. After getting used to block coding, youngsters can go on to text-based coding, which involves creating lines of code.
3) What is a block code example?
A few examples can be motion and sound blocks. Motion blocks are used to tell a sprite to turn or wave its hand to build its movement. Users can command a sprite to take 15 steps forward or turn toward another character by using a certain block code. Developers can use sound blocks to add music or other sorts of sound to a story or game. Children can alter the pitch or volume of sounds with sound blocks.
Comments
Your comment has been submitted