Fun and Easy Coding Lessons for Kids in 2025
Fun and Easy Coding Lessons for Kids in 2025
The digital world is changing. Coding lessonsaren’t just for techies anymore. It’s a key skill for kids now, teaching them the basics of computer science. In 2025, educators design lessons to be engaging, intuitive and accessible, even for young learners, whether it’s elementary coding, easy coding, or more advanced topics.
This blog looks at how coding education is changing for kids, particularly through engaging activities. It highlights what makes learning fun and easy, and it shares ways for parents to support this important journey with programing classes and web coding resources.
Introduction
Coding has moved from niche to core skill in today’s digital world. In 2025, even young learners engage with programming tools at school and home. These lessons focus on creativity and solving real-world problems, utilizing various resources.
These lessons encourage computational thinking among students, blend data science concepts and open pathways to advanced courses in machine learning and software development. This article will guide parents and educators through the best coding lessons for kids in computer science and how to make learning both fun and effective with easy coding techniques and accessible programming classes.
Why Start Coding Early?
Starting coding before middle school helps kids build important skills. These skills go beyond just writing code. When a seven-year-old drags and drops blocks in Scratch to make a maze game, they learn key coding skills. They gain sequencing, pattern recognition, and precise instructions. These are all important parts of computational thinking and the foundation of elementary coding.
In a fourth-grade class, students created a weather-tracking project using block-based coding. They pulled real-time temperature data with Scratch extensions. Then, they calculated daily averages and showed the results in simple bar-chart animations. This type of easy coding project combines fun with practical application.
This hands-on activity made math concepts clear. It also showed young learners that data science starts with clear logic, and that coding lessons can connect different subjects creatively.
How Computer Programming Builds Problem Solving Skills
Early exposure to coding transforms abstract science ideas into interactive experiments. In a typical lesson, kids can program a micro:bit. They make LEDs light up based on light-sensor input. This turns a physics concept into a fun game. Kids start text-based coding, like Python or JavaScript, and they learn coding basics while ready thinking like programmers in structured programming classes.
They tackle new challenges by dividing problems into smaller steps. Then, they test solutions and fix errors. These problem-solving skills apply to all subjects. They assist in writing clear instructions in English class. They also help design experiments in science.
Teaching kids coding at an early age also builds confidence with technology. Visual interfaces make terms like “variable” and “function” easier to understand. This helps learners focus on creative problem-solving rather than just memorizing syntax, highlighting the need to teach coding effectively . As they learn block-based coding, they build logical reasoning skills.
These skills help with machine learning models and software development later. Introducing coding lessons early makes learning fun and engaging. It also builds a strong foundation for future success in STEM and other fields.
Developing problem-solving skills
Coding lessonsencourage kids to learn to code by breaking big challenges into small tasks, helping them grow as independent thinkers. These activities teach young learners to break complex challenges into simple steps, developing strong problem-solving and analytical reasoning, a core benefit of elementary coding programs.
When a child writes a simple loop using programming tools, like block-based coding tools such as Scratch, or practices Python basics in programming classes, they focus mainly on logic and structure. These easy coding exercises make it simple for beginners to grasp essential concepts.
This method reflects scientific processes in data science like gathering information, testing hypotheses, and refining solutions through computational thinking. Such technical skills transform how students approach Math or Science, that turns abstract theories into tangible experiments.
Supporting creativity and logical thinking
Programming is both analytical and imaginative. Kids learn to design their own games, animations and interactive stories by combining logic with creativity, emphasizing the need to learn to code . Starting coding at an early age supercharges creativity, empowering kids to design games, animations and interactive lessons while blending logic with imagination, a skill nurtured in elementary coding and easy coding activities.
As kids quickly prototype ideas, they learn that code is more than just a tool. It’s also a way to express creativity. Through programming classes and web coding projects, they can build digital stories or create amazing interactive projects.
This mix of algorithmic thinking and creative play builds basic ideas for advanced areas like artificial intelligence and machine learning. Educators see that young learners who take part in these activities are 42% more engaged in STEM subjects. They view failures as chances to learn and improve.
Example: A 10-year-old student uses Scratch to create a game. In this game, a character catches falling stars. While practicing coding, the child includes score tracking, sound effects, and difficulty levels. They use if-else conditions, loops, and event triggers for this.
This hands-on interactive lesson teaches problem-solving skills step by step. Next, the student explores Python. They use basic data science to build an image classifier. They do this with a no-code tool, such as Teachable Machine. They train it to recognize hand-drawn shapes with concepts from artificial intelligence. As students shift from Scratch to Python, they learn to test ideas.
They also debug code and improve their solutions. Teachers say this learner was once unsure in math class. Now, they show solid reasoning and confidence in computer science and web development.
Making coding for elementary students a gateway to the digital world
Starting elementary coding at a young age helps kids understand digital tools. This confidence grows as they get older, especially through school experiences. With structured coding lessons, they open the door to our digital world and explore how apps, websites, and robots work.
They gain confidence using everyday technology. They understand terms like "variable","keywords", "classes, "objects" in simple words. This helps them build fluency in programming and in how digital systems work. For middle school students, fluency helps them move smoothly into advanced math and science classes. In these subjects, programming is very important.
As students grow, they gain key skills for future jobs. This includes areas like web development, AI,ML,etc Educators and parents help kids learn coding by offering free resources. This allows children to learn at their own pace. As a result, they build lifelong problem-solving skills.
What Makes Coding Lessons in 2025 Unique
In 2025, coding lessons for kids combine technology and modern teaching methods. They emphasize engagement, personalized learning, and essential concepts. Gone are the days when children memorized syntax rules from textbooks, now, even elementary coding is interactive and tailored to each child’s pace.
Today’s platforms feature AI-driven learning paths. These paths change difficulty based on how each student progresses.
This setup allows young learners to work at their own pace. If a child struggles with loops in Scratch, the system offers mini‑challenges that reinforce computational thinking and problem solving skills through visuals and game‑like rewards. They can also explore web coding basics as part of this journey. This unique approach makes coding easy. It removes frustration and focuses on real understanding instead of rote memorization.
Making Learning Fun Through Coding Lessons and Amazing Projects
Storytelling and animation now anchor the learning process, turning every lesson into an amazing project. Kids start with stories like, “Help the cat find its way home using repeat blocks.” They also create animations that share their own tales.” These text‑based coding and block‑based coding scenarios make coding feel like game development, not a dry classroom assignment.
Platforms inspire learners to write more code and explore programming tools. They combine creativity, character design, and plot choices. This way, learners can experiment with variables and test logic branches while having fun.
Real‑world simulations bring practical relevance to every class. Platforms incorporate scenarios like controlling a virtual robot on Mars, optimizing traffic lights in a smart city, or monitoring climate data on Earth.
These interactive lessons show children how skills translate to fields like environmental monitoring, robotics and predictive analytics. They learn to think in systems.
They see how algorithms can impact the real world. This applies to exploring artificial intelligence or building web projects. Early exposure to these essentials equips students with technical skills and opens doors to future careers in AI, game development and beyond.
Kids Learn Coding Through Teamwork and Collaboration
Collaboration also defines 2025’s approach, turning individual study into a social coding experience. Virtual classrooms let students join coding clubs, share unique projects, and give each other feedback in real time. Educators and teachers lead Hackathons, peer learning sessions, and hour-of-code events. They create a supportive community that reflects real-world software development.
Kids learn to use Git workflows. They also communicate on virtual forums and solve problems together. By focusing on teamwork, resources, and classroom support, today’s coding curriculum prepares the next generation not just to code, but to lead, teach, and innovate.
Example: An eight-year-old uses Scratch to code a Mars rover. They animate the rover with loops and event triggers to avoid obstacles. This helps them improve problem-solving skills and learn computational thinking. Next, they use a text-based coding editor.
They write a Python script that logs simulated sensor data. This introduces data science and predictive analytics. They add a simple machine learning model to improve the rover's "traffic lights." This shows how programming tools, AI, robotics, and web development team up in a fun project.
Types of Coding Lessons for Different Age Groups
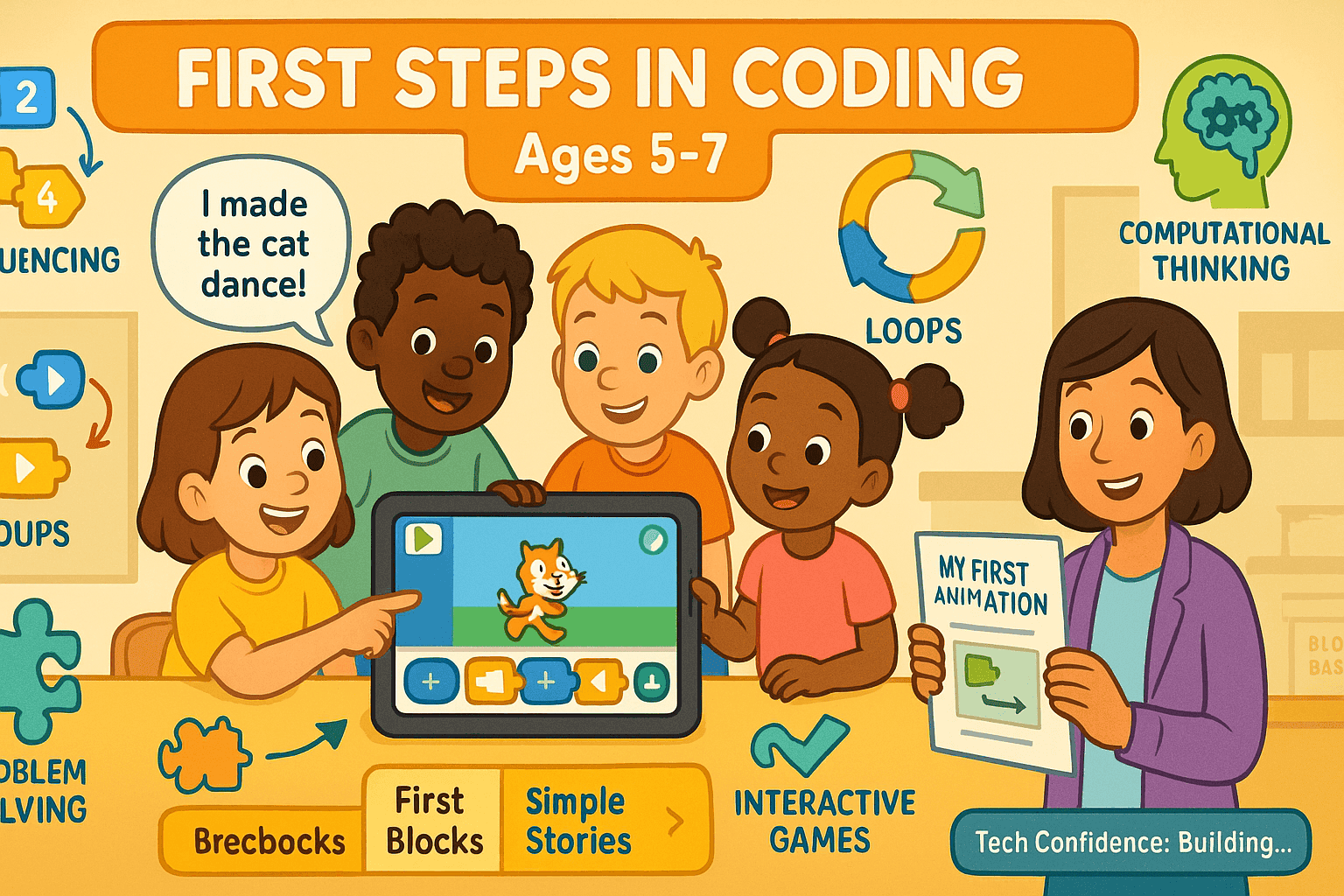
Ages 5–7: Block‑Based Foundations
Young learners begin with block‑based coding on platforms like ScratchJr, where they build foundational concepts through drag‑and‑drop logic. These interactive lessons focus on sequencing, loops, and events. Core programming fundamentals strengthens computational thinking and problem solving without any typing.
Young learners begin with block-based coding lessons on platforms like ScratchJr, where they build foundational concepts through drag-and-drop logic. These interactive activities focus on sequencing, loops, and events. Core programming fundamentals strengthen computational thinking and problem-solving without any typing.
Children snap together colored blocks to create animations and simple games, making every activity feel like fun coding. Teachers integrate amazing projects and free resources into the cs curriculum, allowing each teacher to help kids learn coding basics at their own pace and develop early confidence in technology.
Ages 8–10: Game Creation and Storytelling
Elementary students graduate to Scratch, Blockly or Tynker, where they gain coding knowledge by building maze games, interactive stories, and simple sensors with micro:bit. They explore variables and conditions, learning how to control sprites based on user input.
These gamified coding lessons spark creativity and maintain engagement through art, music, and real‑world simulations. By blending game development with storytelling, kids learn to troubleshoot code and collaborate in virtual classrooms. Educators provide curated free resources and programming tools that turn every project into an amazing project.

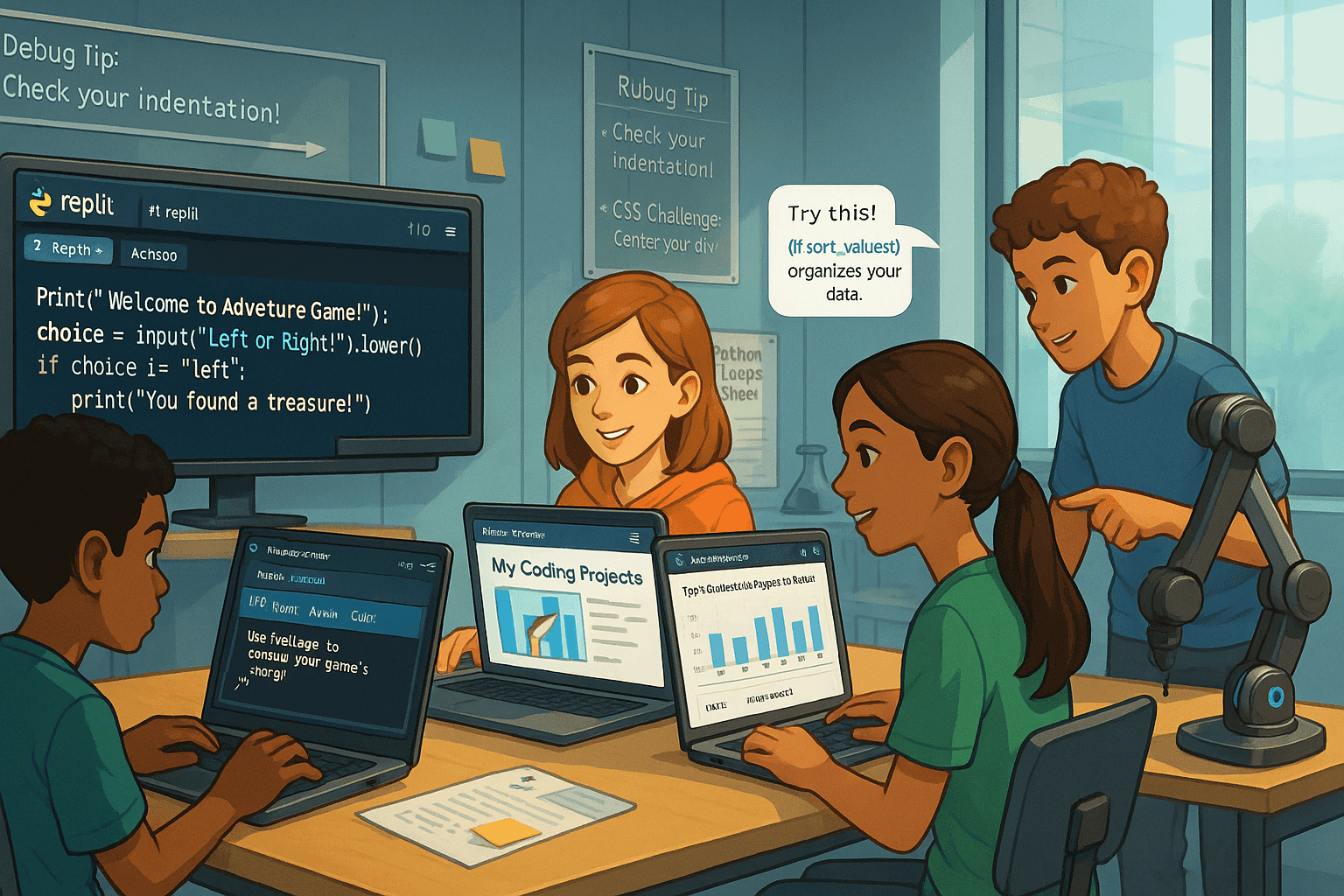
Ages 11–13: Transition to Text‑Based Coding
Middle school marks the shift to text‑based coding in Python and basic HTML/CSS. Replit and Trinket are browser-based editors. Students can type code, run simple websites or make text-based games.
This helps kids learn how code can work with tables, create graphs and analyze data. These are essential for future careers in data science and artificial intelligence. These courses focus on technical and critical thinking skills. They teach students coding in a supportive class setting and with a clear curriculum.
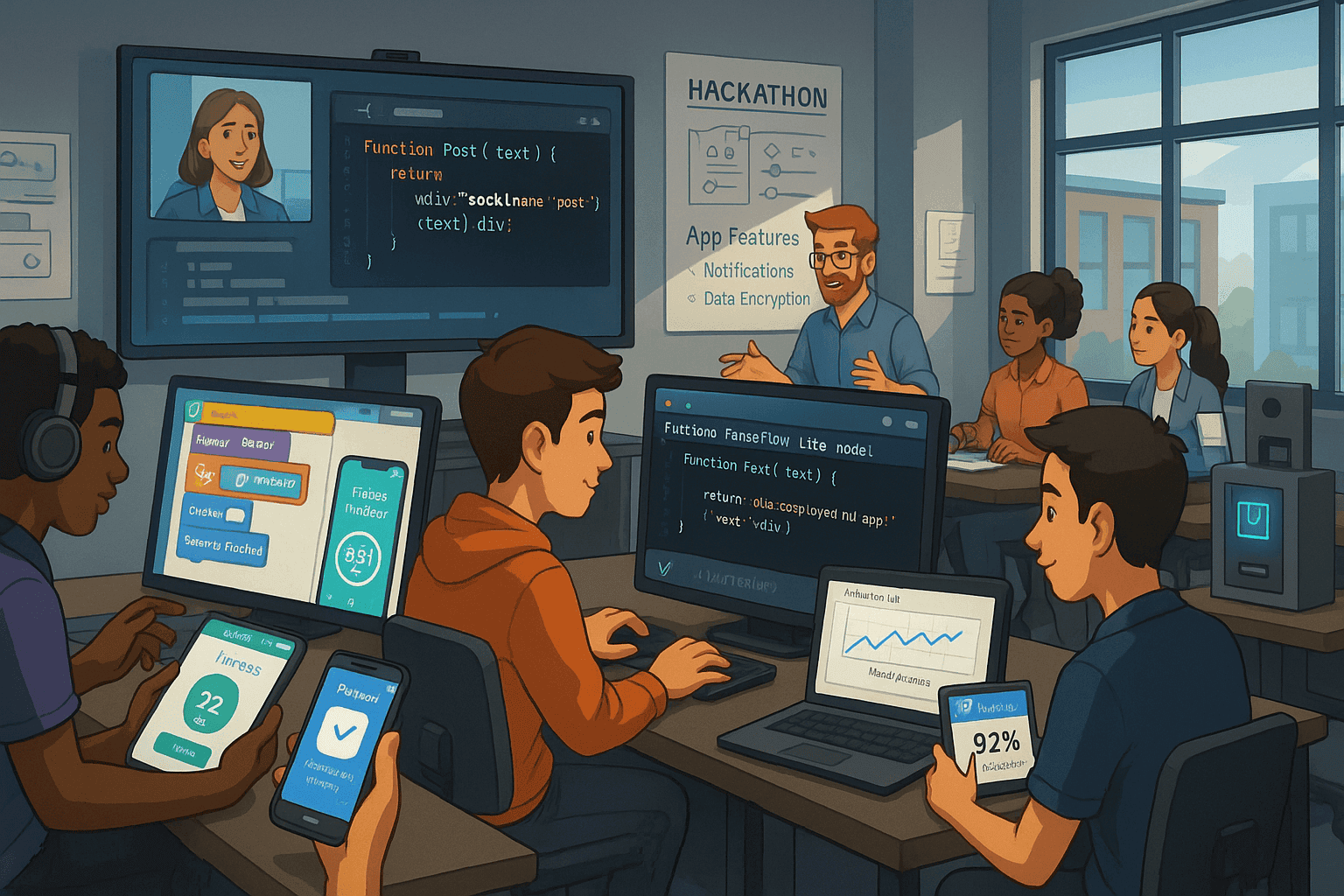
Ages 14+: Real‑World Programming and App Development
High school students learn about JavaScript and Python libraries. They also explore mobile app tools like MIT App Inventor and Thunkable. They work on group projects to create apps that solve real problems. These include a homework planner, fitness tracker, or a mini social network.
This helps them practice collaboration and learn from each other. Many classes teach machine learning models using TensorFlow Lite. They show how to train and deploy simple AI agents. By combining programming tools, interactive lessons, and real‑world simulations, educators equip the next generation with essential skills, preparing them for future programming courses, technical careers and lifelong learning.
Tools & Platforms Making Coding Fun for Kids
The right programming tools turn learning into play. In 2025, platforms support all learning stages. They mix technical skills with fun, user-friendly designs in the curriculum .
Scratch & ScratchJr let kids build animations and games with colored blocks. These platforms feature character libraries, background scenes, and sound effects to enrich projects.
Code.org provides structured courses that follow a curriculum. They include fun challenges like “Minecraft Hour of Code” and “Star Wars: Jedi Challenges.”
Tynker gamifies learning through themed “missions” and digital badges. With built‑in tutorials, kids progress from block code to Python seamlessly.
Thunkable & MIT App Inventor empower older learners to create smartphones apps. Drag-and-drop components link to device sensors and online databases. They demonstrate real-world software development.
Replit & Trinket provide instant, browser‑based Python programming. They enable multiplayer coding sessions. They also include integrated version control. This simulates real software development workflows.
micro:bit & Arduino kits bring code to life with hardware. Kids program LEDs, sensors, and motors. They learn how code works with the physical world through robotics projects.
These tools emphasize hands‑on exploration and keep lessons error‑free through built‑in hints and instant feedback. They also promote process fun, adjusting to each child's skill level . Celebrating each milestone, big or small, boosts confidence and fosters a growth mindset.
Coding Tools for Kids
Platform | Ideal Age | Focus Area | Style |
|---|---|---|---|
Scratch / ScratchJr | 5–10 | Game and animation design | Block-based |
6–14 | Puzzle-based challenges | Block + intro to text | |
Tynker | 7–14 | Gamified learning path | Block → Python |
Thunkable / App Inventor | 10–16 | Mobile app development | Drag-and-drop |
Replit / Trinket | 12+ | Real coding in-browser | Text (Python, etc.) |
micro:bit / Arduino | 10–16 | Hardware & robotics | Block + C/Python |
How Parents and Educators Can Support This Learning Journey
Educators and parents use a method to spark curiosity and build familiarity with coding lessons. A clean corner has a trusted device, simple instructions, and open-ended challenges. These will spark creative thinking while introducing elementary coding concepts.
Little things are done by young learners. They gain confidence on one hand while discovering how imagination ties in with logic through programming.
Basic implementation early on consists of a simple schedule: three short sessions a week, with each lasting under half an hour. That helps prevent burnout while reinforcing conceptual understanding. By developing skills, learners gain experience with different CS curriculum modules.
This journey takes them from block interfaces to text scripts. This design is simply to allow the child to get his basic skills first. It would also motivate them continuously through the hour of code since there would be small rewards.
For older kids and young adults, advanced classes are designed. They have an opportunity to learn about AI, data workflows, and interactive web features.
They test models like image recognition, chatbots that are more human-like, and interactive stories that change as you engage. Everything focuses on the practical.
It prepares the next generation for tech careers and inspires innovative minds. When parents and teachers join together, coding becomes a shared journey. They help kids learn resilience, critical thinking, and lasting enthusiasm.
Building Essential Skills Beyond Code
Coding lessons offer more than programming knowledge like:
Computational Thinking: Kids learn to decompose problems, spot patterns, and design algorithms.
Critical Thinking: Debugging code teaches students to test assumptions and refine strategies.
Collaboration: Peer feedback and team projects foster communication and empathy.
Creativity: Open-ended assignments let learners express themselves through design, storytelling, and art.
Adaptability: As platforms change, students learn new languages and tools. This helps them build resilience for lifelong learning.
These skills help kids face challenges in data science and machine learning. They get ready for future jobs in tech and more. Kids who code learn to value exploration, trying new things, and using facts to reason.
Conclusion
In 2025, coding lessons for kids mix fun exploration with serious learning. Kids start with block-based coding in early grades. Then, they move to text-based languages like Python and JavaScript in high school. They also explore machine learning. This way, every child can connect with coding.
AI-driven adaptive learning paths ensure that each student learns effectively, while gamified challenges and real-world simulations make even easy coding activities exciting and relevant.
Educators integrate these tools into a coherent CS curriculum, teaching critical thinking skills alongside programming techniques in structured programming classes.
They build confidence to navigate a tech-driven world. They also gain a foundation for future careers in web development, game development, and software development. Today starts a journey with fun, interactive lessons. They open doors to endless possibilities.
Frequently Asked Question
What age is best to start elementary coding?
Kids can start elementary coding as early as 5 years old using visual block-based platforms that make learning as playing. Early coding builds problem solving,critical thinking skills as they combine blocks together to create animations and games.
At this stage, simple projects let young learners gain confidence in their coding knowledge and computer science ideas. Starting early means children grow comfortable with digital tools and adopt a curious learning mindset.
Are there any free tools for web coding designed for kids?
Platforms like Scratch, Code.org and W3Schools offer free, interactive lessons that guide kids through HTML, CSS and simple JavaScript. These coding courses use step‑by‑step tutorials and immediate feedback to keep learning engaging.
Children can build small web pages, explore web development and share projects with classmates. With free of cost, parents can encourage coding at home and help kids explore programming tools safely.
How do programming classes differ from casual coding lessons?
Structured coding courses follow a clear curriculum with defined goals, regular assessments from basics to advanced topics. In contrast, simple lessons focus on project-based learning, letting kids explore ideas at their own pace and enhances their creativity.
Formal classes often cover machine learning, game development, etc while exploratory sessions increases curiosity and allow us to play. Both approaches build coding skills, but classes emphasize mastery and technical skills, whereas casual lessons emphasize coding and experimentation.
What makes a coding lesson truly easy for beginners?
A simple lesson uses visual block-based coding. Students can drag and drop commands instead of typing. Step-by-step guidance and interactive feedback help kids correct mistakes instantly.
Projects based on real-world tasks boost motivation and make ideas real. Activities like creating a game or an animated story boosts critical thinking.
How can parents support coding for elementary students at home?
Set a regular time for your child to learn coding lessons. Even 15 minutes a day builds strong habits. Explore interactive lessons together. Choose age-appropriate platforms that match their interests. This can include completed projects, fixed bugs or new skills learned.
Ask questions about their projects. This helps reinforce computational thinking. Also, show enthusiasm for what they created. By staying involved and curious, parents help kids turn coding into a fun, lifelong skill.
Comments
Your comment has been submitted