Teaching Children About Money: 10 Mistakes to Avoid
Teaching Children About Money: 10 Mistakes to Avoid

Introduction to Financial Literacy
Financial literacy refers to that branch of knowledge which deals with financial aspects like money. It encompasses understanding various financial literacy concepts such as
budgeting
investing
saving
borrowing
managing debt
A financially literate person can evaluate and analyze financial products, services and opportunities, thereby making some financial decisions that align with the goals and circumstances of an individual.
Key components of financial literacy for kids include comprehending the basics of personal finance, investments, retirement, and money management. This could assist in long-term financial security through investments, additional resources and retirement savings.
It also involves being aware of financial risks and understanding how economic factors can impact personal finances.

Financial literacy for kids includes the ability to critically analyse financial information, compare financial products, and protect oneself against fraud and financial exploitation. Teaching kids about money and educating children about money early on ensures they understand these important concepts. Ultimately, teaching children money skills empowers individuals to navigate the complex cities of the financial world confidently and make choices that contribute to their financial well-being and stability. Financial education for kids is essential in fostering a strong foundation for their future financial independence.
Why Financial Literacy Matters
Financial literacy for kids matters because it helps teenagers to make informed decisions about money. Understanding concepts like budgeting, saving, investing, and that helps in manage their finances responsibly. Prepare them for future independence, ensuring, they can achieve their goals without falling into financial pitfalls.
By learning early, teenagers develop lifelong skills that promotes financial stability and security, enabling them to navigate economic challenges, confidently and build a solid foundation for the future. feature snippet of my financial literacy is important for a teenager teacher or my financial literacy is important for teenagers.

Financial education for kids is crucial as it equips them with the essential skills to manage money wisely, making financial decisions and build a secure future. Eventually, they learn how to handle a savings account.
Following are the points that highlight why financial literacy is important for teenagers:
Empowerment: Financial literacy empowers teenagers to manage money, effectively, make smart spending choices and plan for their future.
Independence: For financial independence as they transition into adulthood, ensuring they can handle expenses responsibly.
Avoiding debt: Understanding financial concepts helps teenagers avoid those traps and make informed decisions about borrowing and credit.
Goal achievement: Set goals enables them to set and achieve financial goals whether it’s saving for college starting a business or buying a car
Building wealth: Early financial education plays the groundwork for building, long-term wealth to savings, investments, and financial planning.

Financial literacy is important for students in the USA and Canada because it helps them with essential skills in navigate the complexities of personal finance and make informed decisions about money management. In today's interconnected world, financial decisions impact everything from education costs to the time in planning, being financially, literate is more important than ever.
Reasons to integrate financial literacy into education curriculum in the USA in Canada is essential because:
Personal financial management: Financial literacy for kids allow students to budget effectively, manage debt responsibly and save for future goals. The skills of foundational for achieving financial stability and independence later in life.

Consumers awareness: Understanding financial products and services helps students avoid predatory practises and make sound choices when borrowing money or investing in products like:
credit cards
loans
mortgages
Economic stability: A financially literate population contributes to overall economic stability by reducing household financial stress, and promoting responsible, spending and saving habits.economic stability: a financially literate population contributes to overall economic stability by reducing household financial stress, and promoting responsible, spending and savings habit and saving habits. This gives them confidence to earn money.
Career readiness: Financial literacy prepare students to negotiate salaries, understand, employee benefits, packages and plan for career transition period. The skills are essential financial literacy prepare students to negotiate salaries, understand, employee benefits, packages and plan for the career transition period. The skills are sensual for navigating the modern job market period The modern job market period.
Entrepreneurship and innovation: For aspiring entrepreneurs, financial literacy is crucial, business, planning, secure, funding and managing cash flow effectively.
Understanding financial products and services helps students avoid predatory practises and make sound choices when borrowing money or investing in products like credit cards.
Financial literacy is crucial for establishing better spending habits, instilling confidence, and equipping kids with real-world skills to manage financial goals and milestones.
Importance of Teaching Financial Skills Early
Teaching kids about money to teenagers early is crucial for their long-term financial well-being and success as adolescents transition into adulthood, they face an increase in responsibilities and decisions related to money. By instilling financial literacy, other young age, Ascension, knowledge and skills that will benefit them throughout their lives.
Early financial education provides teenagers with the fundamental understanding of basic concepts like budgeting, saving and investing. These money skills are foundational for managing personal finances effectively.
Secondly, financial education prepares teenagers to make informed decisions about spending saving for goes like education of travel, and eventually managing larger expenses like rent or mortgages.

Furthermore, financial literacy has reduced financial pitfalls such as debt accumulation and overspending. Understanding the consequences of borrowing and lending. Financial literacy program can definitely assist teenagers in overcoming such pitfalls.
Thus, teaching financial skills early fosters a mindset of long-term planning and goalsetting weather, saving for college, starting a business, planning for retirement, teenagers' loan, the value of setting, realistic financial goals and developing strategies to achieve them.
In conclusion, all financial education for kids equips practical skills that are initial for navigating the complexities of modern financial systems.
Benefits of Raising Financially Responsible Kids
The domain of finance is important for children to understand so that they have the ability to manage income, funds, budgets, investments, savings, and purchasing power. Teaching kids about money is crucial because children will never understand the importance of money until they know how to earn money and spend it. They must learn from their real life about financial literacy. A financial literacy program can be helpful in educating children about money and understanding the significance of budgeting and managing resources. Teaching children money skills early on builds a strong foundation for their future financial decisions. Financial education for kids is essential to prepare them for the challenges of managing finances as they grow.

Raising financially responsible children is more than just teaching them the value of money. It is about teaching them essential skills that will serve them well into adulthood. From early budgeting and saving habits to understanding the principles of investment and debt management, fostering financial responsibility lays a strong foundation for their future success. These skills not only empower children to make informed decisions but also contribute to their over-all well-being and confidence as they navigate the complexities of adulthood.
Following are the key steps which describe why it is beneficial to raise financially responsible kids and educating children about money at an early age:
Financial Independence: Teaching kids financial responsibility prepares them to manage their money effectively as adults.
Improved Decision-Making: Financially sound kids are less likely to accumulate debt later in life, leading to better financial stability.
Entrepreneurial Skills: Knowledge about finances can cultivate entrepreneur skills and encourage innovation and risk-taking.
Stress Reduction: Financially responsible students and children will be less stressed related to money management and unexpected financial emergencies.
Career Success: Financial education can help students with better career prospects and negotiation skills, leading to increased earning potential. They will have a zest to earn money and will always inclined towards more money.
Family Legacy: Passing financial education creates a positive family legacy of responsible money management across generations. It makes financial futures secure and reliable.
Charitable Giving: Teaching kids and students about financial literacy can inspire generosity and promote them to make meaningful contributions to charitable causes. Charitable giving does not only introduce students to a brighter side of life as being good humans but it also acts like a social responsibility.
Economic Stability: Students and kids who understand personal finance contribute to a more stable economy by attracting more money.
Reason financially responsible kids use numerous benefits that extend well into adulthood. Teaching kids about money helps instill a sense of financial responsibility, which only aids children in developing essential skills such as budgeting, saving, and identifying the difference between needs and wants. These are the foundational skills for educating children about money and making informed financial decisions throughout their lives, providing them with valuable financial education for kids and lifelong money skills.
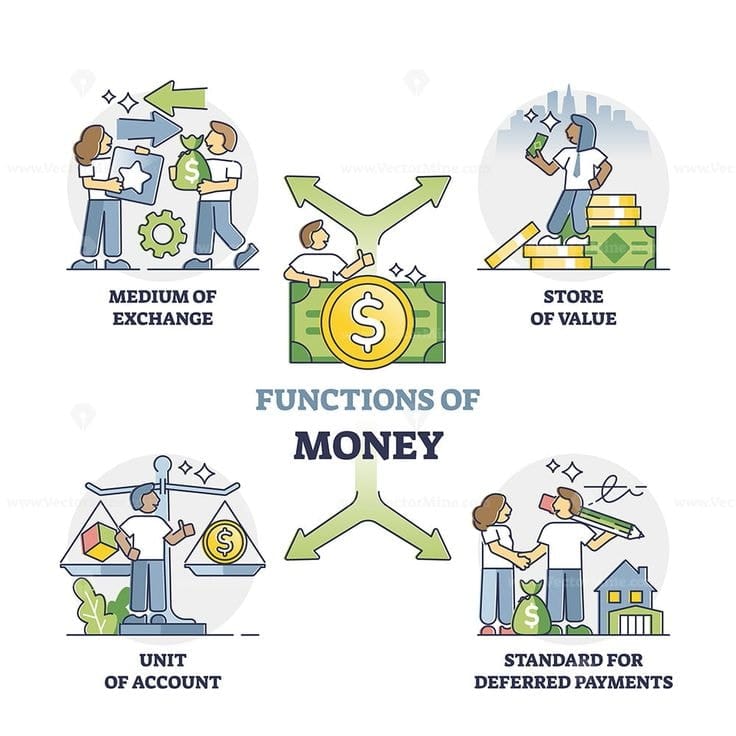
Financial education assists kids in having variety of qualities and self-reliance is one of them. It makes students capable of managing their resources effectively and adapting to financial challenges.
By becoming financially responsible, kids also become money smart, gaining valuable life skills related to saving, investment, and making sound decisions about money.
As students and kids grow, these young individuals develop a deeper understanding of the economic world around them, becoming conscientious consumers, savers, and investors who contribute positively to their communities and beyond.
10 Mistakes to Avoid When Teaching Children About Money
Teaching kids about money is an important aspect of their education that often gets overlooked or underestimated. Educating children about money is crucial as it extends beyond just understanding the value of coins and bills. It also involves developing essential skills that will impact their future economic decisions. Teaching children money skills is an extension of the management of budgets, funds, income, bank accounts, and savings accounts. Financial education for kids plays a key role in preparing them for financial independence and success.
Starting early with financial education can empower children and students to make sound financial choices, manage their resources effectively, and handle responsible habits that will be beneficial for them throughout their lives. It should be a part of their academic lesson plans and learn experience from the everyday life.
However, teaching children and students about money can be challenging, especially if it is not approached thoughtfully. Many parents, teachers and educators make common mistakes that can hinder rather than facilitate their knowledge and experience of financial concepts. Most people don't realise it in their real life until their child falls under the trap and fails to spend money without seeking guidance from the teachers. The first step is to observe such mistakes.
These mistakes range from avoiding the topic altogether to overemphasizing materials, and it can significantly impact a child and a child's financial mindset and behaviours in the long run. It must be taken into account while planning a financial literacy program for your children.
By recognising these pitfalls, a head start should be made by taking smart steps to make children and students delve into financial literacy program and financial education.
Here are ten mistakes to avoid when teaching kids, children and students about money:
1. Treating Money as a Taboo Subject
Avoiding discussions about money in the family can lead to misconceptions or unhealthy attitudes towards finances. Children must be made used to checking account and maintain a regular eye on their bank account. Teachers must talk about budget, bills, credit and dollar amount.
Why It’s a Mistake
Avoiding discussions about money can make it a taboo topic, leading to financial illiteracy.
How to Avoid It
Start teaching basic financial concepts, such as counting money and understanding the value of coins and bills, as early as preschool.
2. Avoiding the Topic
Many parents and teachers shy away from discussing money with children, kids and students, thinking that they are too young or that it is a sensitive subject. Starting early and gradually is key.
Why It’s a Mistake
Delaying financial education means missing out on critical early years when kids are most receptive to learning foundational skills.
How to Avoid It
Incorporate money conversations into everyday life, using real-life examples like grocery shopping or paying bills to explain concepts.
3. Not Setting a Good Example
Children learn by observing. If parents and teachers don't manage money well, children may pick up bad habits.
Why It’s a Mistake
Children learn by observing their parents’ habits. Poor financial habits by parents can be mirrored by their kids.
How to Avoid It
Model good financial behavior, such as budgeting, saving, and making informed spending decisions.
4. Ignoring the Importance of Saving

Without paying attention to savings, children may struggle to understand the value of setting money aside for future needs like retirement and goals.
Why It’s a Mistake
Failing to teach the value of saving can lead to poor money management skills later in life.
How to Avoid It
Encourage kids to set aside a portion of their allowance or earnings into a bank account or piggy bank.
5. Overemphasizing Spending
Focusing solely on acquiring things rather than on financial responsibility and values can lead to poor money management habits.
Why It’s a Mistake
Teaching kids to focus solely on spending can result in impulsive buying and poor financial planning.
How to Avoid It
Balance lessons on spending with teachings on saving, budgeting, and investing. Emphasize the importance of keeping records of money spent and balancing it with saving.
6. Not Explaining the Difference Between Needs and Wants
Children must know the difference between needs and wants so that they can plan their budget accordingly which becomes in favour of their interest.
Why It’s a Mistake
Without understanding the difference, children may struggle with prioritizing their spending.
How to Avoid It
Have discussions about needs versus wants, using practical examples to illustrate the difference. Introduce students to the concept of needs versus wants to help them prioritize their spending.
7. Not Teaching About Budgeting
Why It’s a Mistake
Without budgeting skills, children may not learn how to manage their money effectively.
How to Avoid It
Introduce simple budgeting exercises, like tracking their allowance and spending, to help them understand income and expenses.
8. Avoiding Advanced Financial Concepts
Teachers and parents must address digital money. In today's world, money management happens digitally. Teaching children about online banking, digital payments and security is essential.
Why It’s a Mistake
Assuming advanced concepts like interest rates or credit are too complex can leave kids unprepared for future financial responsibilities.
How to Avoid It
Gradually introduce more advanced topics as children grow, such as the concept of earning interest, the difference between credit and debit, and the basics of investing. It's also crucial to explain credit card debt, its impact on personal finances, and how carrying a balance can affect their credit rating.
Practical Applications of Financial Education
Teaching Kids to Make Smart Financial Choices
Encourage kids to make smart financial decisions and avoid impulse purchases.
Teach kids to appreciate the difference between needs and wants.
Encouraging Savings and Investing
Teach kids to save for big goals and understand the concept of compound interest.
Encourage kids to make smart financial decisions and avoid debt.
Explain the importance of understanding different types of bank accounts, such as savings accounts, checking accounts, and high-yield savings accounts, for managing money effectively.
Comparison Shopping and Smart Consumerism
Teach kids to scrutinize advertising and make informed decisions.
Encourage kids to understand the difference between needs and wants.
Implementing Personal Financial Management
Integrating Financial Education into Daily Life
Teach kids to manage their money and make smart financial decisions.
Encourage kids to prioritize their spending and make smart financial choices.
Using Financial Literacy Curriculum in Schools
Highlight Codeyoung’s financial literacy programs that offer gamified financial skills in a fail-safe environment.
Emphasize the importance of incorporating financial education into the school curriculum to build foundational skills early on.
Online Resources and Tools for Teaching Financial Literacy
Mention Codeyoung’s programs and resources designed to teach kids ages 10 to 14 money management skills.
Provide information on how Codeyoung’s programs are tailored to make learning about finances engaging and effective.
About Codeyoung

Codeyoung is the best platform for your kids to learn coding and financial literacy. We're an internationally certified program by STEM.ORG.
Codeyoung has over 30,000 students across the globe and the top mentors who are diligent and carry an ability to teach children coding and financial literacy in the most simplified manner.
Students also get lifetime access to the learning platform so they can access the course at their convenience and they also have the opportunity to connect with other students across the globe.
Benefits of doing Codeyoung's Financial Literacy Program
Parents get fortnightly updates about their child's performance.
24*7 dedicated student success managers are available for you to ensure you get an amazing experience.
What are you waiting for? Book a free demo now!
Teaching Kids About Money - FAQ
What is the best age to teach kids about money?
There is no perfect age to teach kids about money. Children tend to learn from observation, so parents must maintain healthy financial habits and simultaneously instil the values of financial education for kids in their children. By educating children about money early on, parents can help their children develop the necessary foundation for teaching children money skills that will benefit them throughout their lives.
How do you teach financial literacy in a fun way?
Financial literacy for kids is not a degree, financial literacy program can be broken down into interactive lesson plans which can make it engaging for the children.
What is a financial education course?
Financial education course is basically referred to as a financial literacy program. It is specially designed for kids and students. It is meant to educate children about money and financial terms and practices like saving, budgeting, and maintaining a savings account. This course focuses on teaching children money skills that will serve them in their future. Teaching kids about money at an early age is crucial, and this program aims to provide financial education for kids that will shape their understanding of money management.
Comments
Your comment has been submitted