Understanding Parts of Speech: Types, Functions, and How They Build Sentences
Understanding Parts of Speech: Types, Functions, and How They Build Sentences

Introduction
Parts of speech form the backbone of the English language, guiding new words as on the way they could be put together to represent meanings. With each part of speech assigned a specific role, their functions help construct complex sentences so that ideas could be articulated clearly. Being familiar with these elements of speech also improves communicating skills and the fluency in other languages of writing and speaking.
Let's discuss the eight basic parts of speech and their main categories namely nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Their main categories, definitions, roles, and examples will be discussed to further elaborate how they contribute to the formation of sentences. Once learners understand how they play off each other, they can construct sentences that are meaningful and effective.
What is Part of Speech?
A part of speech refers to proper nouns the role in a sentence that a word plays. Every word was classified according to its roles: naming things, descriptives of speech depending actions, or modifiers that could change other parts of words. With such classification, language is organized, and studies regarding how sentences new nouns are framed and understood become easier. They play their own part in english grammar.
A lexical category of speech refers to a class of words grouped together based on their grammatical and functional properties in a language. It is also known as a part of speech. Each word classes a lexical category has a specific role in the structure and meaning of sentences.
For example, nouns are words for things, places, or persons, whereas verbs (action words) express the action or describe a person or a state of being. Adjectives and adverbs provide additional information through their ability to modify specific noun-s and verbs, respectively. Other parts of speech include conjunctions and prepositions, which enable words and phrases to link together to form relationships in a sentence.
Mastery in parts of speech is quite essential for effective communication. It provides a framework that for speech definitions helps in the analysis of speech definitions and sentence structure and enhances ability to construct clear and specific messages. Therefore, by mastering this core understanding of speech correctly, learners can unlock better performance both in writing and speaking.
Types of Parts of Speech in English
These primary parts of speech are noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. Each type serves a particular function in the structure of a sentence or its meaning.
Here is the list of the eight parts of speech in English grammar:
Nouns: Name people, places, things, or ideas (e.g., mango, honesty, USA).
Pronouns: Replace nouns to avoid repetition (e.g., they, them, he, she, it).
Verbs: Express actions, occurrences, or states of being (e.g., eat, walk, study).
Adjectives: Describe or modify nouns and pronouns (e.g., red, tall, intelligent).
Adverbs: Modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, indicating how, when, where, or to what extent (e.g., yesterday, gracefully, very).
Prepositions: Show relationships between a noun (or pronoun) and another word (e.g., at, from, on).
Conjunctions: Connect words, phrases, or clauses (e.g., because, and, but).
Interjections: Express emotions or reactions (e.g., alas, wow, oh).
Each part of speech plays a unique role in sentence construction, speech definitions and communication.
Different Parts of Speech in English with Examples
Nouns

Nouns are words that name people, places, things, or ideas. They act as the subjects or objects in sentences. For instance, "dog," "city," and "happiness" are nouns. Nouns can be concrete, singular, plural, proper, or common.
Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Other nouns have different functions and uses.
Indefinite or indefinite articles are a type of article used to refer to non-specific or generic nouns. In English, the indefinite articles are "a" and "an". They indicate that the noun being referred to with indefinite articles is not unique or previously known to the speaker or listener.
A definite article is a type closed class of article used to refer to a specific or particular noun that is already known to the speaker and listener or is uniquely identifiable. In English, the definite article is "the definite article".
Pronouns
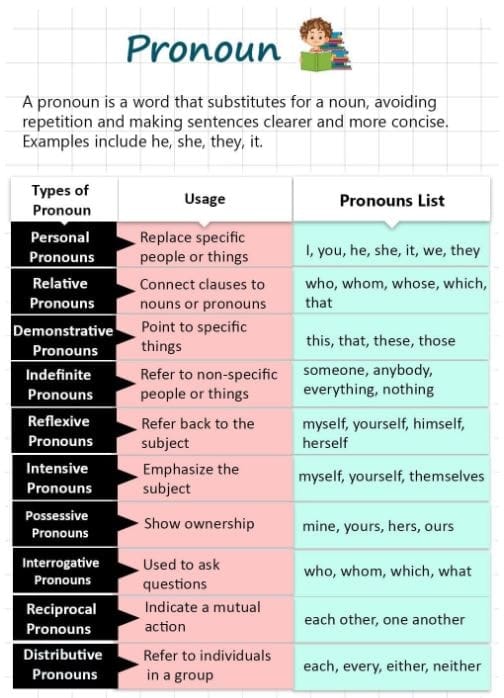
Pronouns refer to common nouns to avoid repetition and make sentences more smooth. Examples common nouns include new words "he," "she," "it," "they," "this," and "who." Pronouns help in maintaining the clarity as well as brevity of a sentence.
PossessivePronouns
Singular:
mine, yours, his, hers, its
Plural:
ours, yours, theirs
Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and the object of a sentence are the same person or thing. They reflect the action of the verb back onto the subject.
Singular: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself
Plural: ourselves, yourselves, themselves
Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative personal pronouns that are used to point to a person, specific people, places, or things, either near or far in distance or time.
Singular: this, that
Plural: these, those
Verbs

Verbs are words that describe actions, events, or states of being. They are crucial in sentence construction because they tell what the subject does or undergoes. Examples include "run," "is," and "think." Verbs can also show tense, mood, and voice.
Types of Verbs
Auxiliary verbs or helping verbs
Transitive verbs
Intransitive verbs
Modal verbs
Linking Verbs
Action verbs
Adjectives

Modifiers of the proper nouns, and personal pronouns: Adjectives provide more information about the proper nouns, or pronoun. For example, in "a red apple," "red" is the adjective that tells more than one part about the other nouns in, "apple." Adjectives answer "what kind?," "which one?," and "how many?"
Many adjectives are used to modify a noun or a pronoun.
Adverbs

Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs to describe in which way, when, where, or to what extent something is done. For instance, english words "quickly," "yesterday," and the word "very" are adverbs. They add precision and depth to sentences.
Adverb describes a verb or an action.
Prepositions

Prepositions indicate relationships between a noun (or pronoun) and another word in the sentence. They often show direction, location, relative position, time, relative position, or means. Examples include "in," "on," "at," "by," and "with." Prepositions generally function within prepositional phrases like "on the table."
Conjunctions

Conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses to build more complex and cohesive sentences. Coordinating conjunctions like "and," "but," and "or" join elements of equal importance, for example, while subordinating conjunctions like "because," "although," and "if" introduce dependent clauses or subordinate clause.
Subordinating Conjunctions:
Subordinating conjunctions are words or phrases that connect a dependent (subordinate) clause to an independent (main) clause, showing the relationship between the the two clauses. These subordinating conjunctions introduce the dependent clause and indicate how it relates to the independent clause in terms of time, cause, condition, contrast, or other relationships.
Interjections
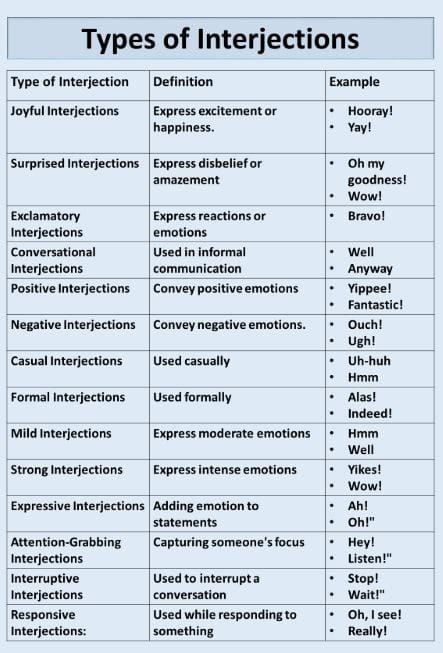
Interjections are words or phrases that show great emotions or reactions. They usually stand alone and are punctuated with an exclamation mark, like "Wow!," "Oh," and "Oops!" Interjections add emotional content to communication. It is used to express and describe strong emotions.
Open Class versus Closed Class
Open class includes:
Nouns: Represent people, places, things, or ideas.
Examples: car, happiness, smartphone (new terms like "selfie" or "metaverse" often arise).
Verbs: Indicate actions, occurrences, or states.
Examples: run, code, Google (e.g., "Google" became a verb).
Adjectives: Describe or modify nouns.
Examples: blue, trendy, eco-friendly.
Adverbs: Modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
Examples: quickly, digitally, sustainably.
Closed word classes include:
Pronouns: Replace nouns.
Examples: he, she, it, they.
Prepositions: Indicate relationships between words.
Examples: in, on, under, about.
Conjunctions: Connect clauses or phrases from other languages.
Examples: and, but, because, although.
Determiners: Introduce nouns.
Examples: the, a, some, each.
Auxiliary Verbs: Help main verbs express tense, mood, or voice.
Examples: is, have, do, will.
Interjections: Express emotions or reactions.
Examples: oh, wow, ouch.
How Parts of Speech Build Sentences
Each part of speech plays a specific noun critical role in the speech correctly constructing sentences, creating a cohesive and meaningful structure. Here is an in-depth explanation of parts of speech and how each contributes:
Nouns and Pronouns: These words are essential as they provide the subjects and objects of a sentence. The subject, often a noun or pronoun, indicates what or who the sentence is about, while the object receives the action. For instance, in the sentence "The teacher explained the lesson," "teacher" is the subject, and "lesson" is the object. Pronouns (e.g., "he," "she," "they") replace nouns to avoid repetition, streamlining communication. For example, "John went to the store. He bought milk" uses "He" to replace "John."
Verbs: Verbs form the predicate of a sentence, which states what the subject does or its condition. They are central to sentence construction because they express action (e.g., "run," "write") or states of being (e.g., "is," "seems"). For example, "The dog barks loudly" uses "barks" to describe the action of the subject "dog." Verbs also convey tense, mood, and aspect, providing temporal and emotional context to sentences.
Adjectives and Adverbs: Adjectives add specificity by modifying nouns and pronouns, answering questions such as "What kind?" "Which one?" or "How many?" For instance, "a red apple" specifies the type of apple with "red." Adverbs, on the other hand, modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, answering "How?" "When?" "Where?" or "To what extent?" For example, in "She sings beautifully," the adverb "beautifully" describes how she sings. Together, adjectives and adverbs enrich the sentence with detail and nuance.
Conjunctions and Prepositions: Conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses, creating complex and compound sentences. Coordinating conjunctions (e.g., "and," "but") link equal elements, while subordinating and coordinating conjunctions (e.g., "because," "although") introduce dependent clauses. For example, "I stayed home because it was raining" uses "because" to link the cause. Prepositions show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word, often indicating direction, location, or time. For instance, "The book is on the table" uses "on" to indicate the relationship between "book" and "table."
Interjections: Interjections inject emotion and emphasis, often standing apart from the main sentence structure. They are typically used to express surprise, joy, anger, or other strong feelings. For instance, "Wow! That’s incredible" uses "Wow" to convey amazement. Although they do not directly contribute to the grammatical structure, interjections add a layer of emotional expression.
By understanding the unique roles of each part of speech, learners can create complex sentences, that are grammatically correct and richly expressive. The interplay of these elements ensures complex sentences that are not only structurally sound but also effective in conveying precise meaning.
Examples of Parts of Speech in Everyday Language
Parts of speech are fundamental to constructing meaningful sentences, and their use in daily language reflects how we communicate ideas, actions, and relationships. Each category of word plays has a unique role, contributing to the structure and flow of speech or writing. Let’s explore their roles with examples from everyday language.
Nouns are the backbone of most sentences, representing people, places, things, or ideas. For instance, in "The cat sleeps," cat is a noun that names the subject performing the action. Nouns can be specific (John, Paris) or general (book, river), making them essential for identifying subjects and objects in a sentence.
Verbs express actions, states, or occurrences. They are indispensable for conveying what is happening in a sentence. In the example, "She sings beautifully," sings is the main verb, that describes her action. Verbs can also indicate states of being, such as is in "He is tired," where the verb connects the subject to its condition.
Adjectives and adverbs add descriptive detail, enriching communication. Adjectives like quick and brown describe nouns, as seen in "The quick brown fox." Adverbs like gracefully modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, offering information about how, when, or where actions occur, such as in "She speaks softly."
Prepositions and conjunctions provide structure by linking words and ideas. Prepositions like over in "He jumped over the fence" establish relationships between nouns and other elements. Conjunctions like and or but connect clauses, ensuring sentences flow logically, such as in "She studied hard, but she still failed the exam."
Finally, pronouns and interjections offer clarity and emotional expression. Pronouns like he, she, it replace nouns to avoid repetition, while interjections like wow or oh convey feelings directly. For instance, "Wow, this is amazing!" adds enthusiasm to the statement.
Understanding and identifying parts of speech in daily language helps improve clarity, coherence, and precision in communication. It demonstrates how each category contributes to crafting meaningful and expressive sentences.
Closed Word Classes: are groups of words that have a relatively fixed membership, meaning new words are rarely added to them. These word classes typically serve grammatical functions in sentences, helping to structure language rather than carry specific content.
Closed word classes are essential in modern grammars for the grammatical structure of a language. While they may not carry specific meanings like nouns or verbs, they are crucial for constructing coherent and meaningful sentences. Their stability and functional nature make them foundational elements in any language.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the parts of speech is fundamental for mastering English grammar and effective communication. Each part of speech—nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections—plays a unique role in sentence construction, helping convey clear meaning and structure. Mastery of these elements enhances reading, writing, speaking, & language skills, enabling learners to express themselves with precision and clarity. By recognizing how each part of speech functions, learners can build grammatically correct, engaging sentences and communicate more effectively.
About Codeyoung
Codeyoung is an excellent platform for kids to learn English, combining innovative teaching methods and interactive content to make learning both fun and effective. One of the key features of Codeyoung is its use of games, activities, and multimedia tools to engage young learners. This interactive approach helps to keep children interested and motivated while building their English skills, from basic vocabulary to advanced communication.
Parents in USA and Canada prefer Codeyoung as it also emphasizes practical communication, ensuring that children don’t just learn English in theory but also develop the ability to use it in real-life situations. The platform encourages skills like conversation, storytelling, and public speaking, helping kids become more confident and capable speakers of English. This focus on real-world application is particularly important as it prepares kids to use English in daily interactions, schoolwork, and future career opportunities.
Understanding the Part of Speech - FAQs
How many parts of speech are there in English?
There are eight parts of speech.
What are the 8 parts of speech in English?
Nouns
Pronouns
Verbs
Adjectives
Adverbs
Prepositions
Conjunctions
Interjections
Why are parts of speech important in English grammar?
Parts of speech are fundamental to understanding and mastering English grammar because they provide the basic building blocks for constructing meaningful sentences. Each part of speech plays a specific role in a sentence, helping to convey meaning, establish relationships between words, and create clarity in communication.
Meaning and Precision
Sentence Construction
Flexibility in Expression
Grammatical Relationships
Understanding Sentence Types and Tenses
How do parts of speech help in forming sentences?
Parts of speech are essential in forming sentences because they define the role of each word, ensuring clarity and coherence. Here's how they contribute:
Nouns – Act as subjects or objects, providing the main idea
(e.g., The cat sleeps).
Pronouns – Replace nouns to avoid repetition
(e.g., She loves reading).
Verbs – Indicate actions or states of being, forming the core of a sentence
(e.g., He runs daily).
Adjectives – Describe nouns, adding details
(e.g., The tall building is impressive).
Adverbs – Modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs to provide more information
(e.g., She spoke softly).
Prepositions – Show relationships between nouns and other words
(e.g., The book is on the table).
Conjunctions – Connect words, phrases, or clauses
(e.g., I like tea and coffee).
Interjections – Express emotions, often standing alone
(e.g., Wow! That’s amazing!).
By understanding and using parts of speech correctly, sentences become structured, meaningful, and grammatically correct.
What is an example of each part of speech?
Here’s an example for each part of speech:
Noun – The dog barked loudly.
(dog = person, place, or thing)
Pronoun – She loves to read novels.
(she = replaces a noun)
Verb – They play soccer every weekend.
(play = action word)
Adjective – The blue car is fast.
(blue = describes the noun "car")
Adverb – He ran quickly to catch the bus.
(quickly = describes the verb "ran")
Preposition – The keys are on the table.
(on = shows position)
Conjunction – I wanted to go, but I was too tired.
(but = connects ideas)
Interjection – Wow! That was an incredible performance!
(wow = expresses emotion)
How can I identify parts of speech in a sentence?
To identify parts of speech, start with the noun, which is the subject (e.g., dog, city). If a word replaces a noun, it's a pronoun (he, they). Find the verb, which shows action or state (run, is).
Adjectives describe nouns (red car), while adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs (runs quickly). Prepositions show relationships (on the table), and conjunctions connect words or clauses (and, but). Interjections express emotions (Wow! Ouch!).
By analyzing how each word functions, you can easily determine its part of speech.
Can a word function as more than one part of speech?
Here are some unique examples of words that function as different parts of speech:
Wave
Noun: The wave crashed against the shore.
Verb: She waves goodbye to her friends.
Sharp
Adjective: He used a sharp knife to cut the fruit.
Adverb: She turned sharp to avoid the obstacle.
Set
Noun: He bought a set of tools.
Verb: Please set the table for dinner.
Adjective: She has a set routine every morning.
Fair
Adjective: The decision was fair to everyone.
Noun: We visited the book fair last weekend.
Adverb: He played fair and won the game.
Down
Preposition: She walked down the stairs.
Adverb: He fell down suddenly.
Adjective: She’s feeling a bit down today.
Verb: He downed his coffee in one gulp.
Why are parts of speech important in English grammar?
Structure of Sentences: Parts of speech define how words function in a sentence.
Clear Communication: They help convey meaning and relationships between words.
Grammar Consistency: Understanding parts of speech ensures correct sentence construction.
Writing Improvement: Proper use of parts of speech enhances writing clarity and flow.
Language Skills Development: They are fundamental for reading, writing, and speaking proficiency.
Understanding Word Functions: Parts of speech help distinguish between verbs, nouns, adjectives, etc.
Language Flexibility: Knowledge of parts of speech allows for varied and creative sentence structures.
Comments
Your comment has been submitted