Why Coding Games is the Best Way to Teach Kids Computer Programming
Coding often seems abstract and scary when taught in traditional ways, which can affect the overall education experience. But coding games make it fun, interactive and engaging. Kids learn coding by mixing play with problem-solving and using technology. This helps them also grow their creativity, persistence and logical thinking in fun and engaging ways.
Traditional teaching sometimes overwhelms beginners with syntax and rules. Coding games, on the other hand, help students build coding skills step by step with diverse resources. They create a safe environment where failure means “try again” instead of losing marks. Kids love the fun of play, and teachers see steady progress. This changes coding from a subject to fear into an adventure to explore.

Introduction to Coding Games and Teaching Computer Programming
Coding games are interactive activities designed to teach programming through play. Students solve in-game challenges to explore loops, logic, and conditions, gaining valuable knowledge in the proces . This approach encourages community interaction instead of just memorizing. They quickly see how computer science connects to real problem-solving.
For example, a puzzle might require moving a character across a grid. To succeed, a child must create a program using steps, loops or conditions. They practice sequencing and debugging without realizing they are mastering core coding skills.
In schools, teachers often use these flexible platforms in the CS curriculum. They help support different skill levels. Beginners work with drag-and-drop blocks, while advanced learners practice python or JavaScript. By making learning coding interactive, games transform abstract ideas into visible, repeatable results, providing a new way to engage students.

How Coding Games Build Coding Skills and Fit CS Curriculum
A good computer science curriculum mixes ideas, practice and reflection. Coding games give students practice and quick feedback. They teach core skills such as sequencing, logic and debugging. These skills connect to the school syllabus. Teachers can pick game levels that match what they are teaching.
For example, a level on loops fits with lessons about repetition. A level with variables supports work on math expressions or data. Games also give clear results, such as completed levels and earned badges. This helps teachers track progress and adjust lessons.
Many platforms let students move from block coding to text coding. Kids may begin by snapping blocks in a puzzle, then move on to writing the same steps in Python or JavaScript. This step-by-step path makes the shift smoother and keeps students interested as they grow. Game projects also fit well with project-based learning. Students can build small games, share their code and explain their designs. These activities are the kind of meaningful work that a strong computer science curriculum values.

Why Computer Science Needs Playful Learning Methods
Computer science is usually seen as a serious subject. However, playful learning can make it more fun and easier to understand, showcasing the power of games in education. Blending coding games with regular teaching allows kids explore core computer science concepts. They can learn about loops, variables, and algorithms without feeling stressed. Playful methods enable students of all skill levels connect with technology easily and enjoyably.
Teachers say kids learn better through games. This helps them be more creative, solve problems better, and feel more confident when facing challenges. Students don't just memorize theory; they practice coding in real-world contexts. This makes learning an adventure. This approach aligns with modern classroom resources. Interactive platforms and projects encourage exploration.
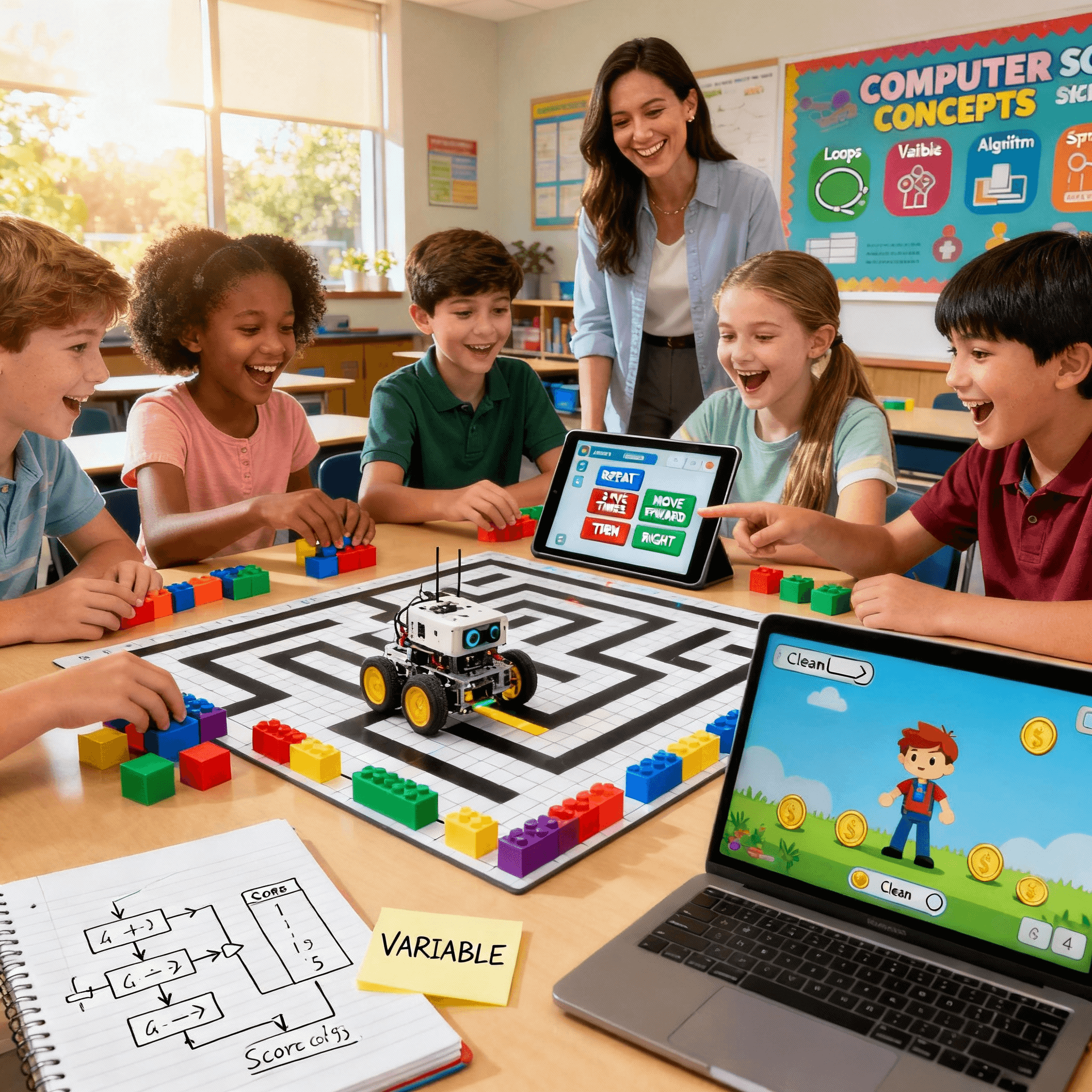

High Engagement Level of Coding Games with Kids
Children are generally interested in games. Challenges and rewards keep them motivated. Coding games use this interest to teach them in a simple manner. Each puzzle solved builds confidence, and feedback helps students learn from mistakes. Teachers can also guide them with extra tips.
Games feel different from worksheets. Stories and missions make learning more engaging, enhancing the image of coding as a fun activity. Kids can replay levels, earn badges, and share their progress. This fun approach encourages them to practice outside of class, giving teachers more time to cover more challenging computer science topics.
Many teachers believe coding games should be part of the classroom. They make learning enjoyable while still teaching important skills, turning lessons into active practice with programming.

Research-Proven Benefits of Coding Games in Learning
Reports show that coding games improve memory and problem-solving. They encourage trial and error, which builds persistence. This skill is important in computer science, writing, and everyday life, paving the way for a successful career. Students who learn coding through play often do better in math since both use logical thinking.
Games give feedback right away. Instead of waiting for a graded worksheet, students see if their code works instantly. This helps them learn faster and remember more.
Some studies also show gains in creativity. Students create their own solutions, proving that coding games teach more than just coding. They help students grow as problem-solvers, designers, and thinkers—skills that matter in school and in the workplace.

Real Programming Languages and Tools Learned Through Coding Games
Many coding games introduce real-world tools. Beginners begin with blocks. Then, they start coding in Python or JavaScript. This ensures that play connects directly to professional languages.
Students practice debugging, project creation and collaboration. These skills reflect real-world developer environments. Platforms often include courses or structured training paths where kids move from simple puzzles to full coding projects. This smooth path goes from basic operations to advanced programming.

Comparison with Traditional Methods of Teaching Coding in Schools
Traditional lessons often focus on rules and syntax first. This can be hard for beginners, especially when teachers don’t use different teaching methods. Coding games do the opposite: students first use logic in context, then learn the syntax that expresses it.
That change leads to faster curiosity, more practice and better retention. Teachers who pair a short targeted lesson with a related game see deeper understanding and higher exam performance than those who rely on lectures alone.

Transferable Skills Learned from Coding Games
Coding games build more than code. They teach problem solving, persistence, planning and creativity skills that apply across subjects. Students learn to breakdown a big problem into steps, test ideas and iterate. These skills support math, writing and science.
Logical reasoning, debugging and pattern recognition
Collaboration through shared projects and peer review
Creativity in designing solutions, art and story-driven code
Making Coding AI Accessible for All Students
Today, AI is changing many industries and creating new jobs. To help kids prepare for the future, we need to make AI easy to learn through fun and practical methods. Coding games and interactive websites help students understand AI better.
Using games and AI tools that adapt to the learner allows even beginners to learn difficult topics step by step. These platforms give quick feedback, clear instructions, and support teachers in class. Kids solve puzzles, work on projects, and find new ideas. This makes AI less scary and more familiar.
The goal is to make learning AI flexible so that every child can explore and engage with it. This should happen in school, after-school activities, and online courses. We can make AI fun and educational, giving young learners confidence. This will help them join the global community of innovators.

Suitability of Coding Games for Different Age Groups
Coding games adapt to all ages and skill levels.
Younger students (grades 1–4): Use block-based puzzles to learn sequencing.
Middle grades: Use adventure-based games with variables and loops
Teens: Practice with Python or JavaScript to create projects
Beginners of any age: Can join free platforms that make learning coding accessible
This flexibility makes coding games AI accessible, meaning they scale for individuals and classrooms with diverse needs. Teachers can select games that match the curriculum and skill level, ensuring both beginners and advanced coders are challenged with suitable partners.
Conclusion
Coding games make computer science easy and fun. They teach coding concepts through fun challenges. The program matches current curriculum and helps students progress smoothly. Learners start with beginner blocks and move on to real languages like Python and JavaScript.
Games provide measurable practice for teachers and schools, boost motivation and stronger transfer to other subjects for students. Games for students build confidence and spark creativity. They also teach coding skills that are vital for future studies and careers. Use games for introductory lessons. Then, add brief, focused instruction. Let students explore, practice, and create. This prepares them for future jobs in industry-based companies.

Frequently Asked Question
How do coding games help kids build problem-solving skills beyond programming?
Coding games work like puzzles that need planning, testing, and fixing. Kids learn to break big problems into small steps, check their answers, and use logic. These skills carry over to math, science, and other subjects. They also build creativity, persistence, and confidence, while helping students grow in coding and computer science
Can coding games be used as supplementary tools alongside formal school curriculums?
Yes. Coding games work well with computer science classes. Teachers use them to review lessons, give practice, and support students at different levels. Many platforms connect game levels to school standards and include resources for teachers and parents. Schools often start with block coding and then move to Python or JavaScript, linking play with real code.
How do coding games adapt to different learning paces and styles of kids?
Coding games have levels, instant feedback, and challenges that adjust to each student. Beginners can use blocks, while advanced students can write code in Python or JavaScript. Hints, retries, and step-by-step tasks help different learning styles. Teachers and parents can also choose specific tasks to fit each child’s needs and keep them interested.
What role do mentors or instructors play in guiding kids while using coding games?
Mentors and teachers connect game tasks to real coding lessons. They explain code when students move from blocks to text, show how to fix mistakes, and give clear feedback. They also set projects, encourage teamwork, and help students turn play into useful practice. Their support builds confidence and helps kids use coding skills in bigger projects.
How can parents track the progress of their kids when learning through coding games?
Most platforms have dashboards and reports that show levels finished, badges earned, and skills learned. Parents can check projects, time spent, and teacher notes to see progress and where help is needed. Many games also suggest next steps and extra challenges. These tools help families see growth and stay connected with school learning.